semantics
Purpose
Finds documents that contain words connected with the arguments by a certain relationship in semantic network.
Semantic network is a knowledge representation in the form of graph which consists of vertices that denote objects and edges that denote relationship between the connected objects. Sets of objects and links are usually domain specific. For example, an automotive industry semantic network might contain vertices that represent different types of vehicles (truck, minivan, supercar…), components (engine, wheels…) or manufacturers and edges labelled "is_part_of", "is_manufactured_by", "consists_of", etc.
By default, two semantic dictionaries are included in PA:
-
Lexical database WordNet that contains words grouped into sets of synonyms (called synsets) and describes several types of semantic relations between them, such as
-
meronym (A is meronym of B, if A denotes part of B, for example "roof"→"building");
-
holonym (A is holonym of B, if A has B as part of itself, for example "building"→"roof");
-
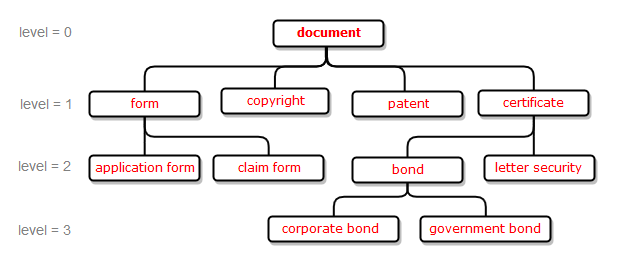
hyponym (A is hyponym of B if A denotes a subclass of B, for example "certificate"→"document");
-
hypernym (A is hypernym of B if A denotes superclass of B, for example "document"→"certificate");
-
antonym (A is an antonym of B if A and B denote opposite concepts, for example "increase"-"decrease").
-
-
PA Default Semantics Dictionary that contains several types of products, technologies, product components and manufacturers (mainly for Healthcare industry) and describes several types of relations between them, such as
-
consists_of (link from product to component);
-
constitutes (link from component to product);
-
has_effect (link from drug to effect);
-
has_name (link from product to alternative name);
-
is_effect (link from effect to drug);
-
is_name (link from alternative name to product);
-
produced_by (link from product to manufacturer);
-
produces (link from manufacturer to product).
-
Arguments
The first optional argument max_level accepts a non-negative integer and defines maximum allowed distance between argument and its related synsets in semantic network.
The second required argument relation_type defines one or more semantic relation types defined in the selected semantic dictionaries. To specify several types of relations it’s necessary to combine their values using vertical bar (for example, hyponym|meronym).
The function also accepts optional named parameters as follows:
-
dictionary:="Name1|Name2|…" indicates the dictionaries to look up. Specified dictionaries must be selected in the node’s properties.
-
synset_id:="id" is used to process only selected meanings (synsets) of the lexeme that belongs to several synsets.
For example, in the WordNet dictionary lexeme "foundation" is included in several synsets, such as
-
"lowest support of a structure" (synset_id = 73795D9D6636B718);
-
"the basis on which something is grounded" (synset_id = 021FD50938EAD67);
-
"an institution supported by an endowment" (synset_id = 95294AEAEDA64D28).
To specify several synsets, it’s possible either to combine their values using vertical bar (for example, synset_id:=95294AEAEDA64D28|73795D9D6636B718) or to add several parameters "synset_id_n" where n is a parameter index (for example, synset_id:="95294AEAEDA64D28", synset_id_1:="73795D9D6636B718").
-
-
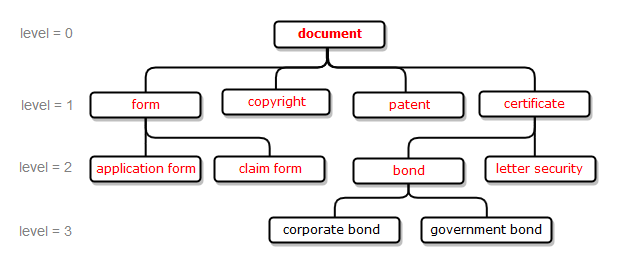
max_level:=N has the same meaning as the first argument max_level and defines maximum allowed distance between argument and its related synsets; synsets located further than N levels from the argument are excluded from the output (see example 2). By default, max_level:=1 is used for the relation types hypernym, holonym, antonym and max_level:=20 for all other relations types.
-
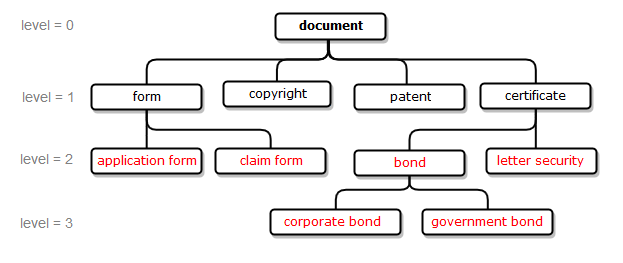
min_level:=N - defines minimum required distance between argument and its related synsets; synsets located closer than N levels from the argument are excluded from the output (see example 4). By default, min_level:=1 is used for the relation types hypernym, holonym, antonym and min_level:=0 for all other relations types. If "min_level" is set to 0, function returns argument itself too. To exclude argument itself from search results, "min_level" should be set to 1 (see example 6).
-
level:=N function returns only related synsets located N levels from the argument (equivalent to min_level:=N, max_level:=N).
-
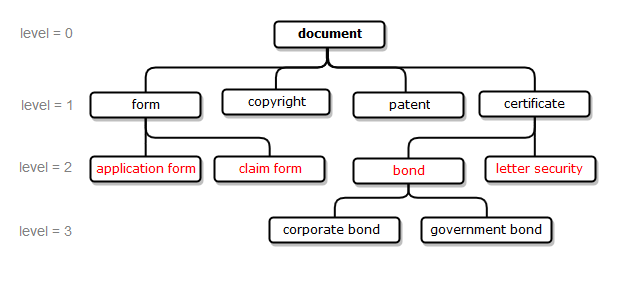
collect:=last/all - "collect:=last" means that function returns only the synsets of the higher(lowest) level (see example 3). "collect:=all" means that function returns all possible synsets. By default, collect:=last is used for the relation types hypernym, holonym, antonym and collect:=all for all other relations types.
-
attribute is used to filter the synsets by their attribute values (see example 7). Each synset may contain attributes, each attribute may contain one or more values.
If the attribute name does not contain spaces and other special characters the simple notation is allowed: attribute-name:="value1[|value2[|…]]". Otherwise the following notation is required: attribute:="attribute-name=[value1[|value2[|…]]]". In this notation the indexes should be used: attribute_1, attribute_2 etc.
If multiple filters are set, only synsets that fulfill all specified conditions are matched.
-
pos:=yes/no allows POS-dependent/independent search on the basis of POS-tags stated in the ontology (see example 9). By default pos:=yes.
-
stem:=yes/no allows to take into account/ignore the form of the word. If stem:=yes, then dictionary entries will be treated as word forms and normalized (see example 10). By default, stem:=no.
-
allow_punct:=yes/no regulates whether punctuation marks are allowed within the synset.
Nested semantics() functions can be used to search for arguments connected by a path that consists of several relation types (see example 8).
Examples
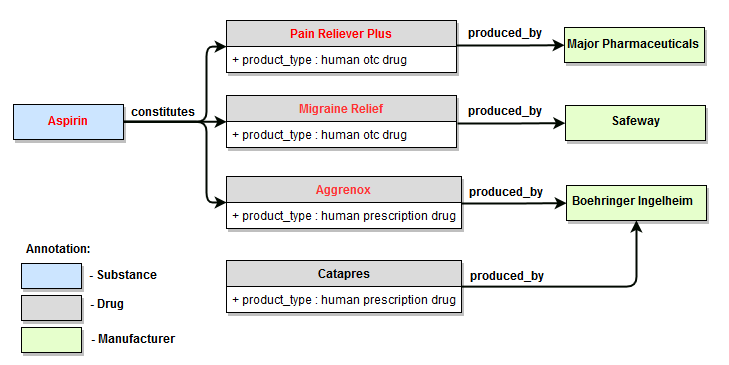
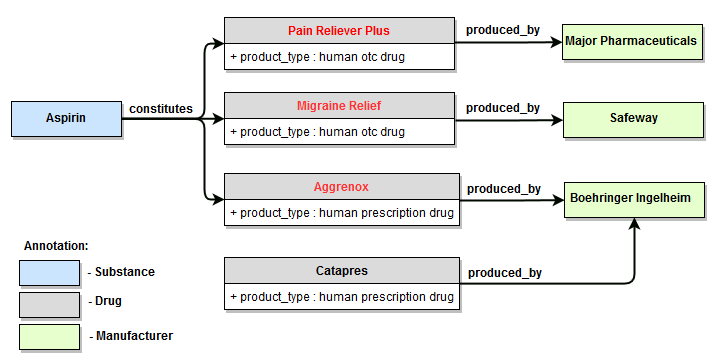
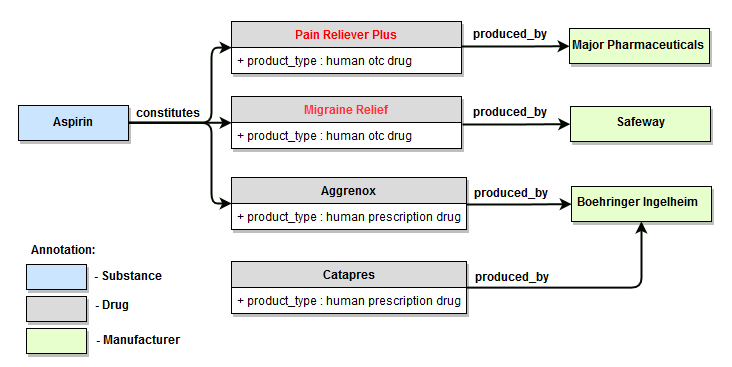
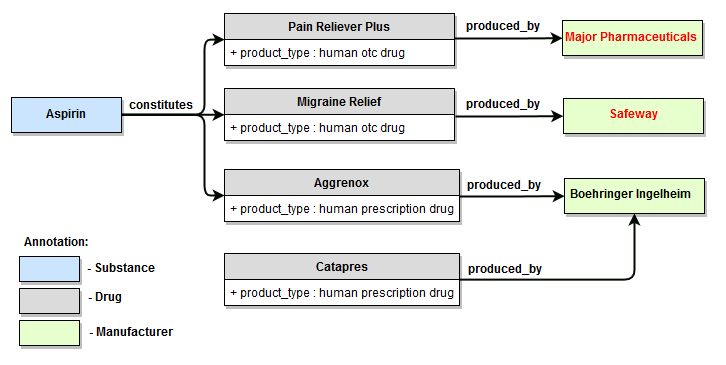
Examples 1, 2, 3, 4 are illustrated using fragment of the WordNet dictionary that describes relationship of type hyponym for the concept of "document"; examples 5, 6, 7, 8 are illustrated using fragment of PA Default Semantics dictionary that describes relationships between several aspirin-containing drugs and their manufacturers.